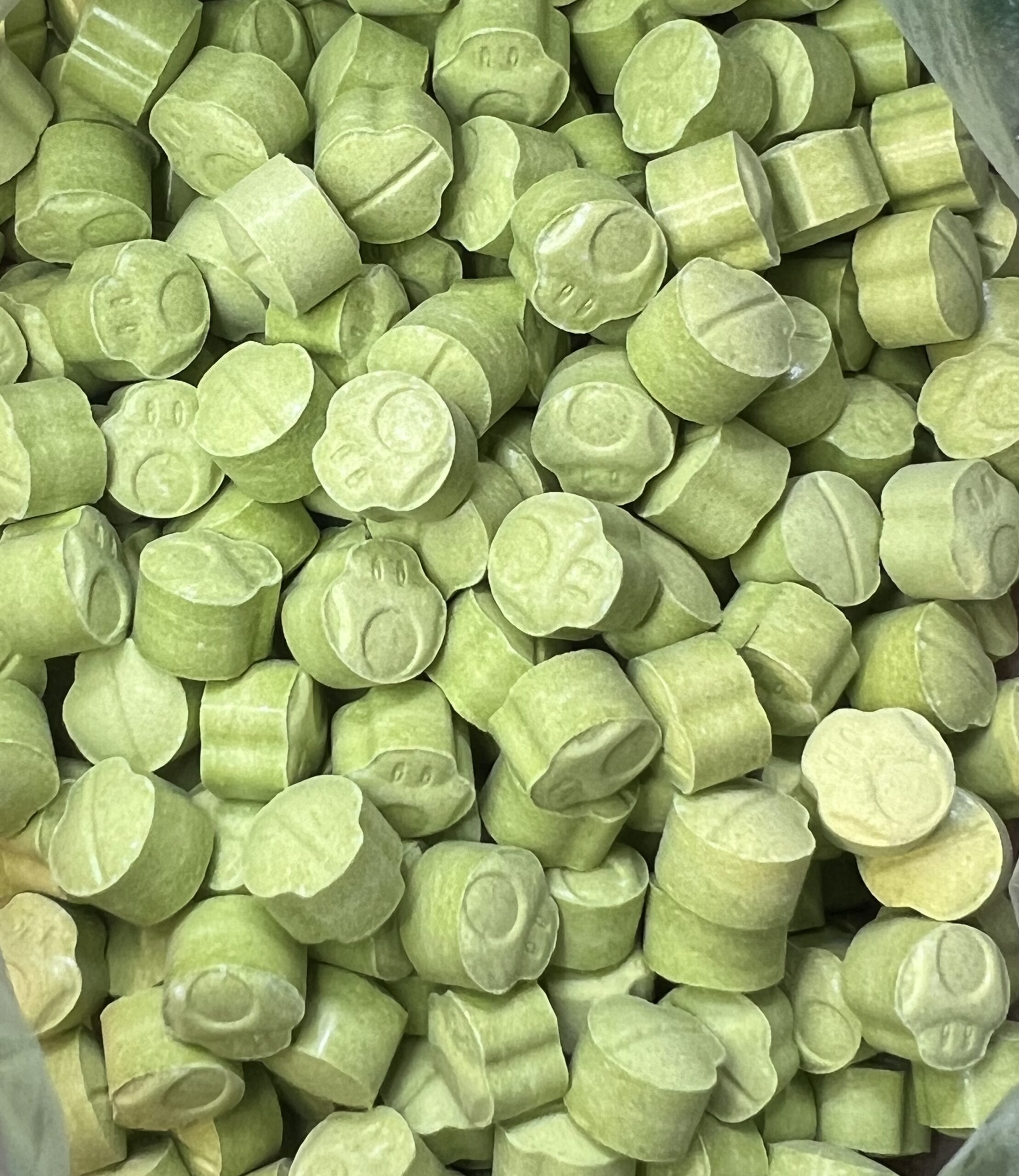
Rebel Moon Mario Pills 80Mg MDA + 60Mg Caffeine + 5Mg Cialis
$13.00 – $190.00
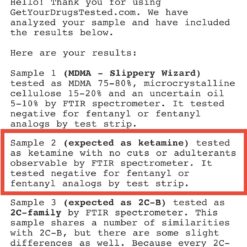
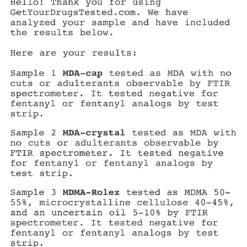
3,4-Methylenedioxyamphetamine (also known as MDA, and Tenamfetamine, or colloquially as “Sally”, “Sass”, or “Sass-a-frass”) is a synthetic entactogen of the amphetamine chemical class. It produces long-lived entactogenic, stimulant and mild psychedelic effects that include stimulation, anxiety suppression, enhanced feelings of empathy, affection, and sociability, and euphoria when administered.
As with MDMA, MDA is thought to act primarily as a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor and releasing agent.[citation needed] However, MDA is significantly more potent by weight and subjective intensity relative to MDMA. It also has a notably longer duration (six to eight hours instead of three to five) and produces more traditional serotonergic psychedelic effects (such as visual distortions) along with appreciably higher activity on dopamine, which is also believed to be responsible for the greater degree of neurotoxicity it produces.
| Quantity | 1 pIll, 10 Pills, 20 Pills |
|---|
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Referral Program
For each friend you invite, we will send you a 15% off coupon code that you can use to purchase or get a discount on any product on our site. Get started now, by sharing your referral link with your friends.
Related products
Pills / Capsules
Pills / Capsules




















Reviews
There are no reviews yet